You’re halfway through a build when an inspector walks onto the site. One crew’s already working at height, a subcontractor from another trade is unloading materials, and you’re fielding questions about who’s responsible for what. If safety expectations aren’t clear, what follows can involve costly delays, frustrating rework, or even a stop-work order.
OSHA training can prevent that disruption. While you might think it’s just about ticking a compliance box, it can be instrumental in keeping your jobs running smoothly.
Knowing the difference between OSHA 10 and OSHA 30 helps you put the right training in the right hands, so your crews are clued in on safety expectations while your supervisors know how to manage risk on busy residential sites.
In this guide, we break down the differences between OSHA 10 and OSHA 30 for residential builders working under Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards, so you can make training decisions that support safer sites and more competitive builds.
What is OSHA Training?
In any workplace, safety training is a must. It isn’t just a means to avoid lawsuits; it minimizes workplace injuries and even saves lives.
OSHA training is based on strict standards set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. For builders working on site, it helps address the daily risks that show up across every stage of a construction project.
It could involve moving a ladder, accessing a roof, or exposure to potentially harmful substances like asbestos. When these risks are managed differently from site to site or crew to crew, small mistakes can escalate fast.
These statistics from the OSHA Online Center show the importance of proper safety training:
- Fall protection is the most frequently cited OSHA violation in construction, even though ladders, roofs, scaffolding, and open edges are standard parts of residential builds.
- Bodily reactions to chemicals and substances account for 84% of reported workplace injuries, including exposure to dust, solvents, adhesives, treated timber, and finishes commonly used on home sites.
- In 2024, 89% of companies relied on proactive safety measures such as inspections, audits, and risk assessments to improve their safety management systems.
OSHA training creates a consistent safety baseline by defining which hazards matter on site, how they’re meant to be controlled, and what acceptable practice looks like in reality.
Why is OSHA training important for small home builders?
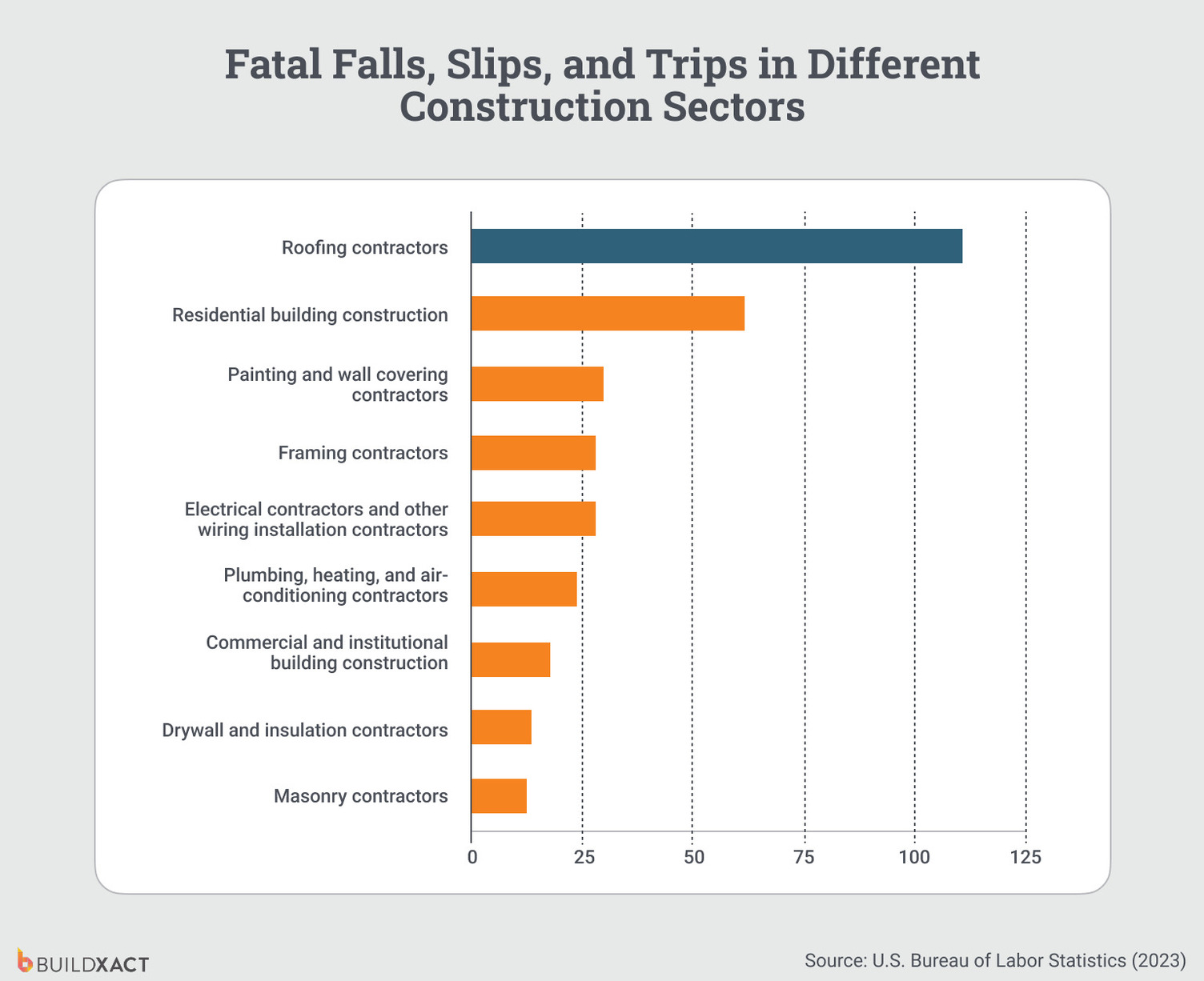
In addition to protecting on-site workers through clear safety standards, OSHA training can also safeguard your business against costly fines and disruptive shutdowns resulting from violations.
Key benefits of OSHA training include:
- Baseline safety standards so every site follows the same minimum requirements
- Lower crew injury risk through clearer hazard recognition and controls
- Consistent subcontractor expectations regardless of trade or experience level
- Required training compliance aligned with OSHA standards
- Fewer fines and shutdowns caused by avoidable violations
- Better hazard awareness during routine, high-risk tasks
- Stronger documentation and protection in case incidents or inspections occur
In residential construction, OSHA training can stop minor safety failures from causing major disruption.
For example, a small crew installing roof trusses relies on OSHA-guided fall-protection practices to manage edge exposure and elevated work, preventing a single misstep from shutting down the build and delaying every trade that follows.
If you’re looking into OSHA training for your business, there are two options available: OSHA 10 and OSHA 30. Next, we’ll explore the difference between these two courses, so you can select the right program for your needs.
What’s the Difference Between OSHA 10 and OSHA 30?
If you’re trying to figure out the difference between OSHA 10 and 30 — and which course is right for you — the answer essentially comes down to one question: What is your position within the company?
If you’re an employee, the OSHA 10 course provides the safety awareness training you need. It’s also the right option if your job mandates OSHA Outreach Training.
If you’re a safety director or a supervisor, then OSHA 30 is the training course you’ll want to undertake.
Both OSHA courses address health and safety hazards in line with maritime, construction, and general industry, and course completion also gives you the ability to train others in these standards.
About OSHA 10 safety training

What is OSHA 10?
OSHA 10 is a 10-hour construction safety course that covers the basics every worker on a residential jobsite is expected to understand. Through the training, you gain a practical understanding of what to watch for, how to work safely, and what’s expected on a construction site.
Who is OSHA 10 for?
OSHA 10 is aimed at entry-level workers, new hires, apprentices, and crew members who need a solid foundation in construction safety. For smaller home builders, it’s often used to bring new team members and subcontractors up to the same safety standard before work begins.
What does the OSHA 10 training course cover?
The course focuses on common residential jobsite risks, including:
- PPE (personal protective equipment) and when it’s required
- Electrical safety responsibilities
- Fire protection and basic scaffolding rules
- Spotting and preventing everyday hazards
- Employee rights and employer responsibilities, including how to file complaints.
It also focuses on aspects such as lifesaving equipment and key areas in home builds, including hand and power tools, excavations, stairways and ladders, and material handling.
What does OSHA 10 allow you to do?

OSHA 10 equips construction workers to carry out basic site tasks safely. On a residential job site, this might include setting ladders correctly, using power tools without unnecessary exposure, and recognizing when fall protection is required during framing.
How long does OSHA 10 take?
The course takes 10 hours, usually spread over two days. Online courses allow for completion in shorter sessions if needed.
How can OSHA 10 be completed?
OSHA 10 can be completed online or in person through authorised providers approved by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
About OSHA 30 safety training

What is OSHA 30?
OSHA 30 is a 30-hour, advanced construction safety course designed for people who run work on-site rather than just perform it. It builds greater skills in identifying hazards, controlling risk, and managing safety across busy construction sites where multiple trades, timelines, and tasks overlap.
Who is OSHA 30 for?
OSHA 30 was designed specifically for field supervisors, safety directors, and foremen. The course is tailored to those responsible for day-to-day decisions that affect how work is carried out and how safely it’s done.
For small residential builders, OSHA 30 is often the right fit for anyone who sequences work or enforces site rules.
What does the OSHA 30 training course cover?
The 30-hour course goes beyond basic hazard awareness to focus on managing safety in more complex conditions, including:
- Hazard control and incident prevention
- Safety leadership and site oversight
- Recordkeeping and employer obligations
- Lead and asbestos exposure
- Ergonomics and confined space work
- Welding, cutting, mechanized equipment, and motor vehicles
What does OSHA 30 allow you to do?
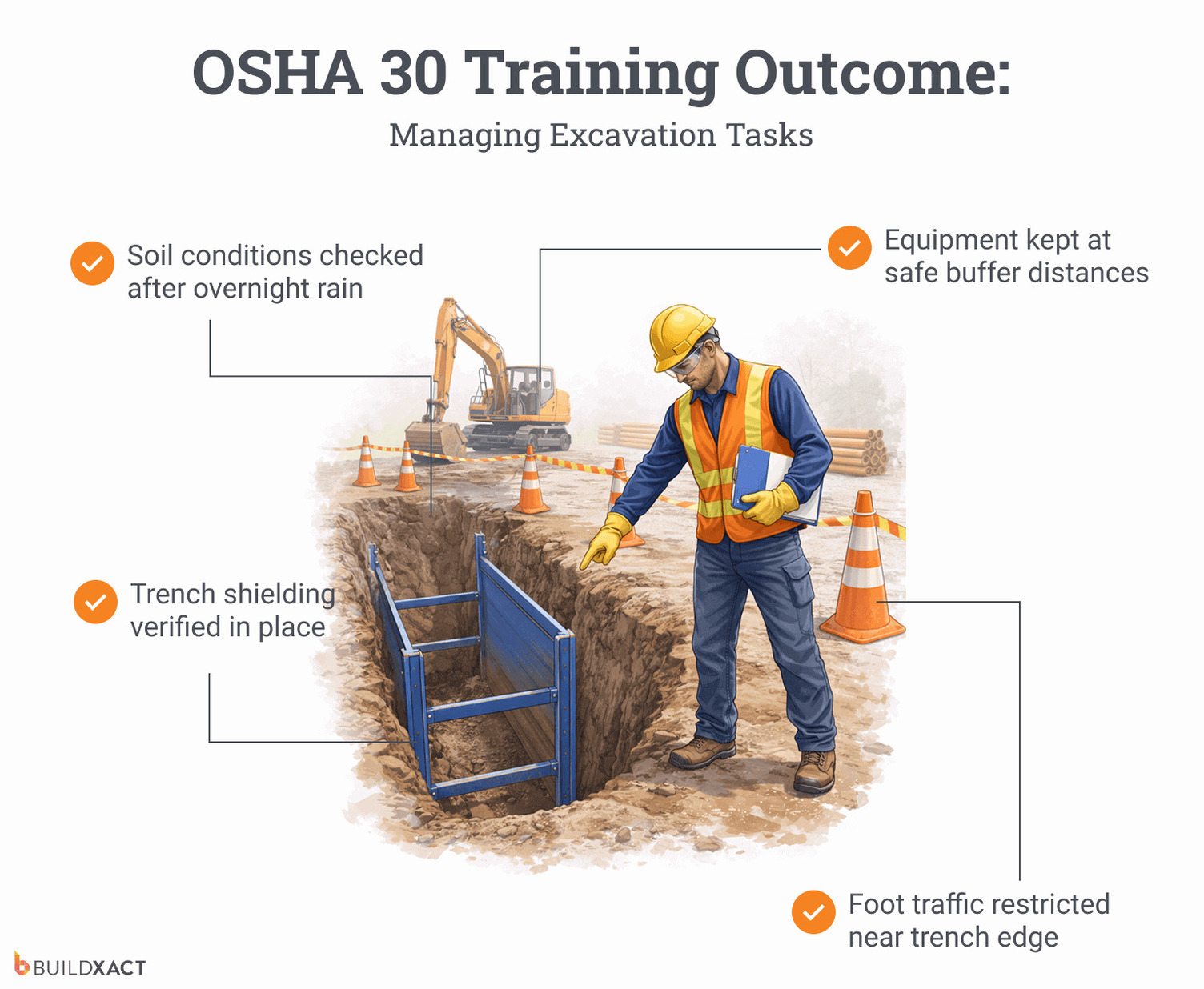
OSHA 30 equips construction leaders to oversee and enforce safe practices on active job sites. On small home builds, that includes coordinating fall protection during multi-trade framing, managing excavation and trench-adjacent work, and enforcing lockout procedures when subcontractors operate powered equipment.
How long does OSHA 30 take?
The 30 hours of training are spread over a minimum of four days. As with OSHA 10, online courses allow training to be completed over a longer period, allowing it to fit around work schedules.
How can OSHA 30 be completed?
OSHA 30 can be completed online or in person through authorised providers approved by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
Are OSHA 10 and OSHA 30 mandatory?
While OSHA 10 and OSHA 30 aren’t required under federal law, many employers recommend them as a sound investment along with other planning methods.
In some U.S. states, laws do require OSHA training for certain roles or types of work. In addition, some unions and employers expect workers to have completed OSHA 10 or OSHA 30 before starting on a job site.
Do Small Home Builders Need Both OSHA 10 and 30?
The short answer is no; most builders and crew members don’t need both.
OSHA 10 is typically sufficient for workers performing day-to-day site tasks, while OSHA 30 is intended for people who supervise work or direct crews. The only time both become relevant is when you move into a leadership role that requires greater oversight of safety.
There’s also no requirement to complete OSHA 10 before taking OSHA 30. Builders and supervisors can go straight into OSHA 30 training if their role requires it, without duplicating training time.
Limits and Restrictions of OSHA 10 & OSHA 30
OSHA courses come with a few limits designed to stop people from rushing through the material or cramming it all into one long day.
Here’s how it works:
- The maximum class length is 7.5 hours in a 24-hour period, even for online classes.
- There should be at least eight hours between training sessions.
- Online courses can take longer than 10 or 30 hours overall, but they still have a six-month completion window.
- If you exceed that time limit, any completed progress is invalidated, and the course must be restarted.
Once you pass the final assessment (you’re allowed three attempts) and receive your certification, it doesn’t expire. That said, some employers may require you to refresh the training from time to time to keep your safety knowledge up-to-date.
How to Find Reputable OSHA Safety Training
While there’s no shortage of safety training providers, the key is to ensure the trainer is appropriately qualified and authorized to provide OSHA training under the law.
The OSHA website has a guide that will help you find approved training providers and education centers in your area.
Safety training is only part of the equation for keeping your sites safe and organized. By connecting your processes, workflows, and documents in a single platform, smart construction software makes it easier to focus on minimizing dangers on the job site.
How Streamlined Construction Management Software Can Strengthen Safety for Small Home Builders
Managing safety on a residential construction site can be hectic at the best of times. Between juggling schedules, trades, and paperwork, risks can become an afterthought until the worst happens.
Intelligent construction management software like Buildxact helps small builders stay on top of site safety, saving admin time and keeping you in control of all the moving parts of your projects.
One source of truth for every job
Centralized documentation and site updates eliminate the version chaos that often leads to unsafe practices. When everyone has easy access to plans and project notes, there’s no room for assumptions that can turn into risky setups and missed controls.
Reliable sequencing that keeps sites controlled
Linked schedules and orders ensure materials and trades arrive in the correct order. That structure prevents rushed workarounds, overcrowded sites, and trades entering areas that aren’t ready or properly secured.
Clear communication across every team member
When everyone’s working from the same information, updates and changes are clear for all to see. Strong communication reduces the risk of conflicting instructions and on-site confusion, which often creates avoidable safety hazards.
Buildxact’s scheduling tool lets you quickly create and assign tasks to your team and contractors, with automatic reminders and attached documents to keep everyone in the loop.
Standardized workflows that reduce variability
Repeatable checklists and processes support small teams to maintain safe, consistent practices from job to job. This standardization reduces the likelihood of people improvising under pressure, leading to safer practices even on busy job sites.
Real-time visibility into site conditions
Progress tracking provides builders with early visibility into delays, clashes, and emerging issues. Identifying problems sooner makes it easier to adjust plans before risks escalate into injuries or stop-work situations.
Buildxact’s Onsite mobile app lets you view and share site progress in real-time from your mobile device, giving you clear visibility into every job.

Less admin, more oversight
Automating repetitive admin means you can swap late-night paperwork for tasks that matter more — like planning and site safety that keep your workers protected and your jobs free of disruptions.
When systems are connected, safety becomes easier to manage day to day, even as workload increases. Builders spend less time reacting to problems and more time keeping sites organized, running without unnecessary risk.
OSHA 10 and OSHA 30: FAQs
How do you know if you need OSHA 10 vs. OSHA 30?
It comes down to your role on-site. OSHA 10 is for workers performing hands-on tasks. OSHA 30 is designed for supervisors, foremen, and anyone directing work or responsible for site safety decisions.
Do you need to complete OSHA 10 before OSHA 30?
No. OSHA 10 isn’t a prerequisite for OSHA 30. If your role involves supervising crews or managing site safety, you can take OSHA 30 directly without completing OSHA 10 first.
Is OSHA 10 required if I already have my OSHA 30?
No. OSHA 30 already covers broader and more advanced safety responsibilities. If you’ve completed OSHA 30, there’s no need to take OSHA 10 as well.
Does OSHA 30 cover OSHA 10?
OSHA 30 goes beyond OSHA 10. It includes deeper coverage of hazard control, leadership, and compliance, making OSHA 10 unnecessary for anyone who already holds OSHA 30.
Is OSHA for US-based construction companies?
Yes. OSHA standards and training apply to construction work performed in the United States. They’re designed around US regulations and enforcement, even if workers or companies operate internationally.
Keep Your Site Team Safe With Smart Construction Management Software
Understanding the differences between OSHA 10 and OSHA 30 helps ensure your team has the proper training to manage job-site hazards. But even the best training can fail to protect if your processes are disconnected.
Smart construction software like Buildxact supports your safety efforts with a solid system that keeps jobs organized at every stage.
By bringing plans, schedules, communication, and progress into a single, connected platform, you reduce confusion, avoid risky workarounds, and maintain better control across every build.
To see how Buildxact helps you keep every project running smoothly, get started for free or book an interactive demo and try it for yourself.